Java基础算法
目录
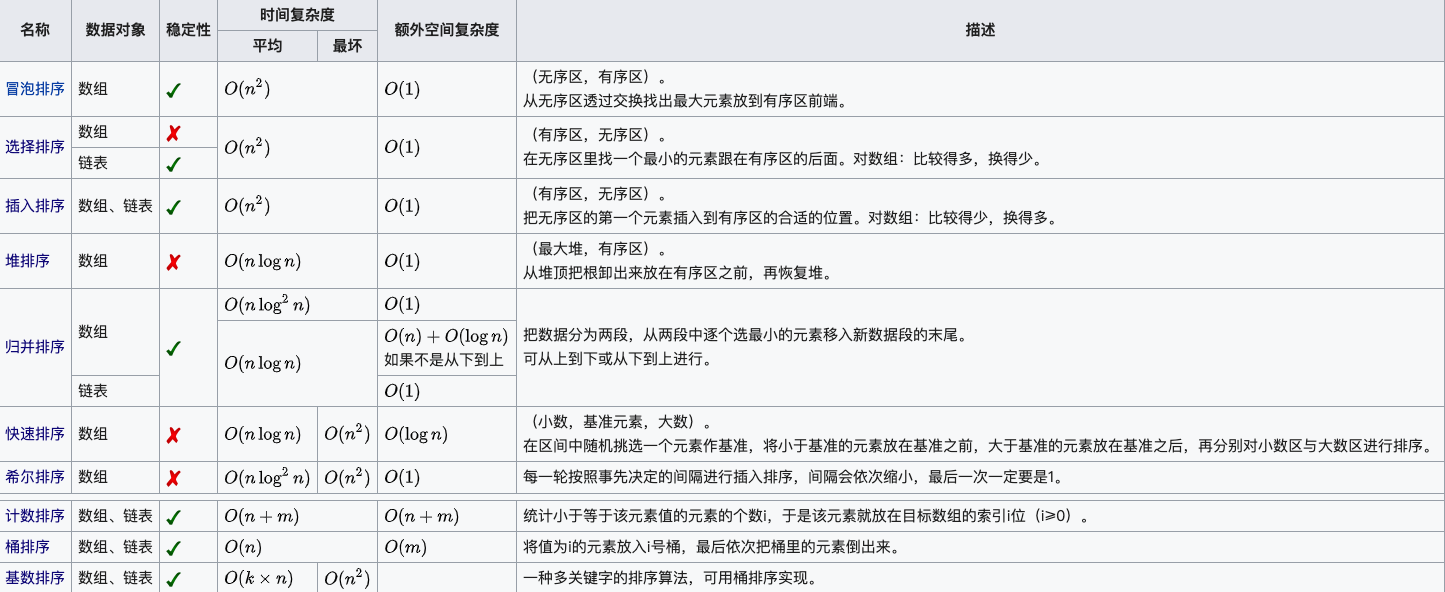
复杂度
冒泡排序
基本原理:
- 对于给定的n个记录,从第一个记录开始依次对相邻的两个记录进行比较,
- 当前面的记录大于后面的记录时,交换位置,
- 进行一轮比较和换位后,n个记录中的最大记录将位于第n位;
- 然后对前(n-1)个记录进行第二轮比较;重复该过程直到进行比较的记录只剩下一个为止。
|
|
选择排序
基本原理:
- 对于给定的一组记录,经过第一轮比较后得到最小的记录,
- 然后将该记录与第一个记录的位置进行交换;
- 接着对不包括第一个记录以外的其他记录进行第二次比较,
- 得到最小的记录并与第二个记录进行位置交换;
- 重复该过程,直到进行比较的记录只有一个为止。
|
|
插入排序
基本原理:
- 对于给定的一组数据,初始时假设第一个记录自成一个有序序列,
- 其余记录为无序序列。接着从第二个记录开始,按照记录的大小依次将当前处理的记录插入到其之前的有序序列中,
- 直至最后一个记录插入到有序序列中为止。
|
|
希尔排序
基本原理:
- 先将待排序的数组元素分成多个子序列,使得每个子序列的元素个数相对减少,
- 然后对各个子序列分别进行直接插入排序,待整个待排序序列"基本有序后",
- 最后再对所有元素进行一次直接插入排序。
|
|
归并排序
基本原理:
- 利用递归与分治技术将数据序列划分成为越来越小的半子表,
- 再对半子表排序,最后再用递归方法将排好序的半子表合并成为越来越大的有序序列。
- 对于给定的一组记录(假设共有n个记录),
- 首先将每两个相邻的长度为1的子序列进行归并,
- 得到n/2(向上取整)个长度为2或1的有序子序列,
- 再将其两两归并,反复执行此过程,直到得到一个有序序列。
|
|
快速排序
基本原理:
- 对于一组给定的记录,通过一趟排序后,将原序列分为两部分,
- 其中前一部分的所有记录均比后一部分的所有记录小,
- 然后再依次对前后两部分的记录进行快速排序,
- 递归该过程,直到序列中的所有记录均有序为止。
|
|
堆排序
基本原理:
- 对于给定的n个记录,初始时把这些记录看作一颗顺序存储的二叉树,
- 然后将其调整为一个小顶堆,然后将堆的最后一个元素与堆顶元素进行交换后,
- 堆的最后一个元素即为最小记录;接着讲前(n-1)个元素重新调整为一个小顶堆,
- 再将堆顶元素与当前堆的最后一个元素进行交换后得到次小的记录,
- 重复该过程直到调整的堆中只剩一个元素时为止,该元素即为最大记录,
- 此时可得到一个有序序列。
|
|
计数排序
基本原理:
- 找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素
- 统计数组中每个值为i的元素出现的次数,存入数组C的第i项
- 对所有的计数累加(从C中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加)
- 反向填充目标数组:将每个元素i放在新数组的第C(i)项,每放一个元素就将C(i)减去1
|
|
桶排序
基本原理:
- 在额外空间充足的情况下,尽量增大桶的数量
- 使用的映射函数能够将输入的 N 个数据均匀的分配到 K 个桶中
|
|
基数排序
基本原理:
- 基数排序是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。
- 由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数。
|
|
讲讲广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历?
- 广度优先遍历:从上往下对每一层依次访问,在每一层中,从左往右访问结点,访问完一层就进入下一层,直到没有结点可以访问为止。
- 深度优先遍历:对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个结点只能访问一次。